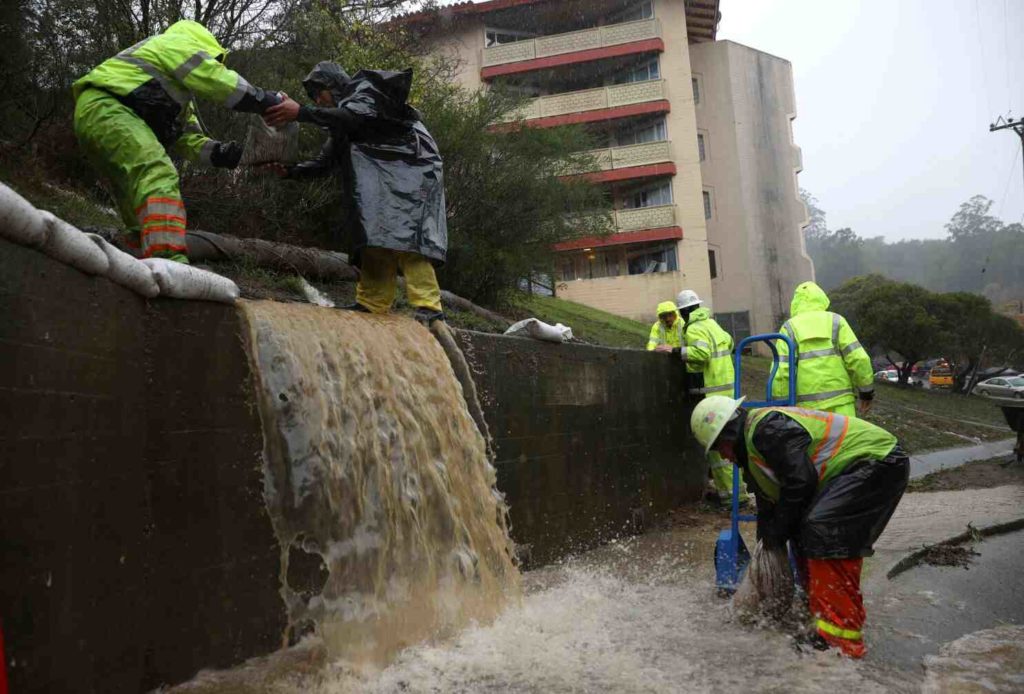
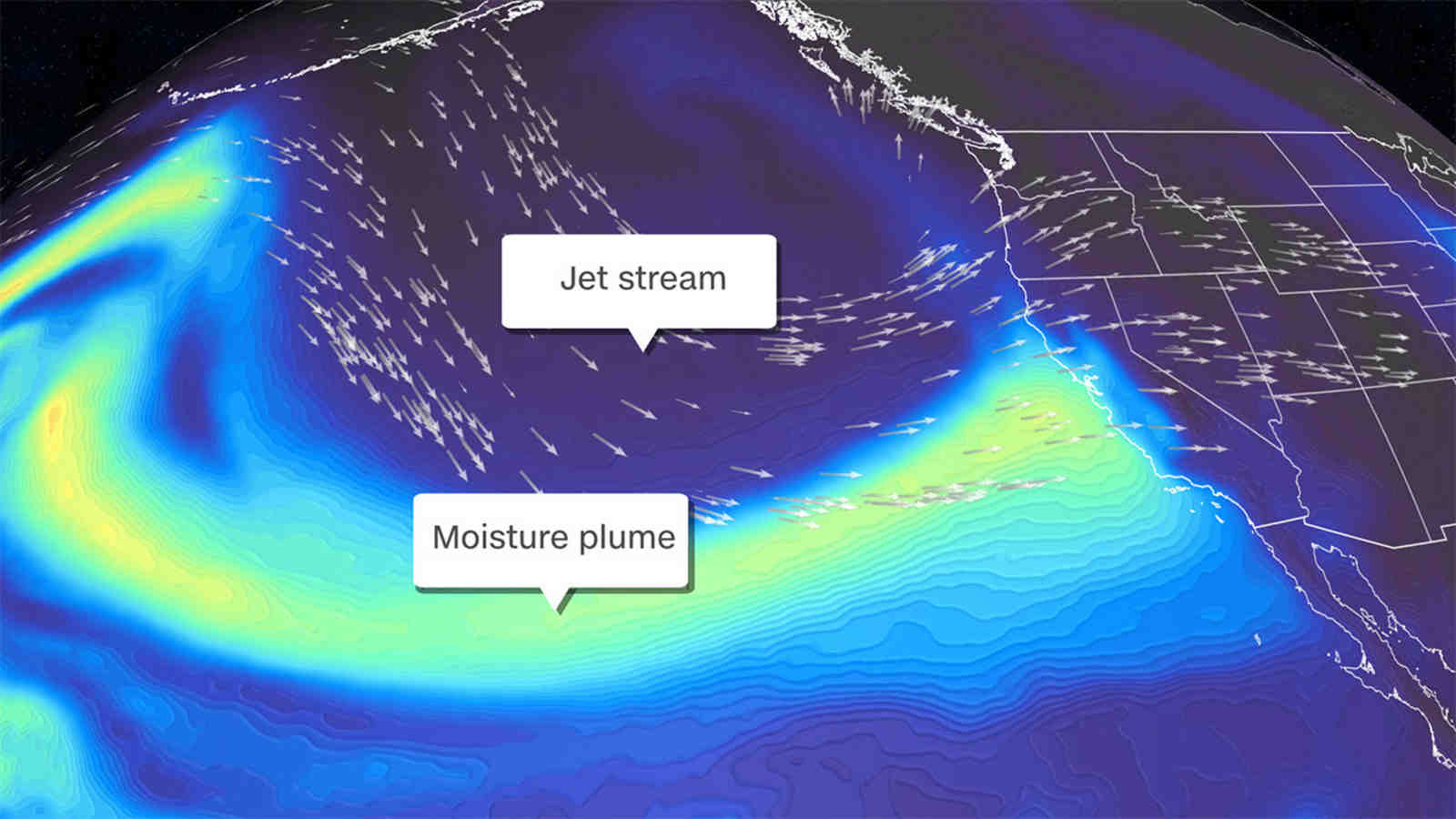
A storm system from Northern California brought rain to parts of Central California on Monday, but Los Angeles remained dry.
Showers have drenched parts of San Luis Obispo and Santa Barbara counties since Sunday. In Santa Barbara County, Sudden Peak received a total of 3.11 inches of rain and Rancho San Julian received a total of 4.07 inches. Santa Maria broke its daily record Monday with a preliminary rainfall of 1.71 inches. His previous record for the date was 0.16 inches, set in 1959.
In San Luis Obispo County, Oceano received a total of 1.74 inches and Arroyo Grande received 2.04 inches during the storm.
The rain has been held off by a slow-moving frontal system that has essentially stalled over the area and is maintaining moisture levels, said David Sweet, a meteorologist with the National Weather Service in Oxnard.
The storm system was forecast to “hang in there all day and not really move,” Sweet said Monday morning, adding that it will eventually weaken and dissipate. It was not expected to move further east of Santa Barbara.
Los Angeles has a 20 percent chance of seeing rain, Sweet said. “There are no surprises here,” Sweet added, even though it’s early in the rainy season.
The rain is coming from a low-lying storm system moving slowly down the California coast, forecasters said.
Rain started the week in the Bay Area, with wet conditions beginning Sunday; scattered showers could last through Wednesday. Lightning strikes were seen in Napa County on Monday.
“We just have an unusual deep low that’s causing some rain,” said Matt Mehly, lead meteorologist for the National Weather Service in the San Francisco Bay Area.
Rainfall totals varied across the area, though the mountains received the most rain, with the North Bay Coast Range getting 2 to 3½ inches, the Santa Cruz Mountains getting as much as 2.2 inches and Mining Ridge getting nearly 4 inches to the mountains of the central coast.
Strong winds and wind warnings led to fears of possible power outages on Sunday. Forecasters predicted some flooding along highways and hazardous local road conditions, including downed trees. There were no weather warnings on Monday.
September is typically the third driest month in California, according to the National Weather Service in the Bay Area. Mehly said the rain was a relief. “We’ve had a historic heat wave with a lot of wildfires, so the precipitation is welcome [across the state] to slow down the fires,” Mehly said. “It won’t be the end, but it’s a step in the right direction.”
Rain showers have brought welcome moisture to the Mosquito Fire, the state’s largest wildfire this year, and aided in the fight against it. As of Monday night, the blaze was 76,290 acres in El Dorado and Placer counties and was 39 percent contained — with an increase of 20 percent on Saturday, according to the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection.
The rain also increased the risk of mudslides and flooding. The hurricane watch will be in effect in the area of the Komarnik fire until 12 noon on Wednesday.
Can a monsoon happen anywhere?

While many of the best-known monsoons are in Asia, monsoons can occur anywhere there is a seasonal difference in temperature between land and water. This is common in tropical and subtropical climates.
What qualifies as a monsoon? So what is monsoon? A monsoon is a large-scale weather pattern that involves a seasonal shift of wind over a region and is usually accompanied by an increase in atmospheric moisture and precipitation. When this particular weather pattern occurs, the time frame is defined as the “monsoon season.”
Do monsoons happen in America?
If you live in the southwestern United States or northwestern Mexico, you may already be familiar with the annual climate phenomenon called the North American Monsoon, especially since some places have had well-above-average rainfall this summer. In fact, this monsoon may turn out to be the strongest ever in some places!
Does North America have a monsoon season?
The monsoon season in North America was first recorded about a century ago and lasts from mid-June to September. It extends from Mexico, which receives as much as 70 percent of its annual rainfall during the monsoon season, into parts of the southwestern United States.
Where do monsoons happen in the US?
The monsoon usually affects Arizona, New Mexico, western Texas, southern Utah, Colorado, and southern Nevada.
Where is a monsoon most likely to occur?
Monsoons are most often associated with the Indian Ocean. Monsoons always blow from cold to warm regions. The summer monsoon and winter monsoon determine the climate for most of India and Southeast Asia. The summer monsoon is associated with heavy rainfall.
Where do the monsoons come from?
The monsoon is driven by the sun, which heats land and the Pacific Ocean at different rates, with land surfaces warming faster than the ocean. Warm earth creates areas of low pressure as hot air rises. Once this pattern is established across the region, winds shift to fill the vacuum.
Where do monsoons occur most often what season are they prevalent?
Asia is known for having two monsoon seasons: the summer monsoon and the winter monsoon. The summer monsoon hits India the hardest, where urban areas prepare for flooding, sometimes up to a meter and a half of water.
What states get monsoon?
Source: Phoenix Weather Forecast Office. In the southwestern United States, the states of Arizona and New Mexico are best known for their seasonal monsoon pattern, but western Texas, southern Colorado, Utah, Nevada, and sometimes even southern California also see monsoon weather.
Does North America get monsoons?
New Mexico is influenced by the North American Monsoon System (NAMS), also called the Southwest Monsoon. While monsoon-related precipitation increases in New Mexico are typically seen in July, the development of the system takes place over Mexico in May and June.
Where does monsoon season occur in the US?
The North American monsoon is a complex weather process that brings moisture from the Gulf of California (and to a lesser extent the eastern Pacific and Gulf of Mexico) over northwestern Mexico and the southwestern United States, causing summer storms, especially at higher elevations.
What is the Southern California rainy season?

Almost all of Southern California’s precipitation falls between October and April.
What is the rainiest month in Southern California? The rainiest month in Los Angeles is February, with an average rainfall of 3.3 inches. The annual rain-free period lasts for 5.7 months, from April 25 to October 16. The least rainy month in Los Angeles is July, with an average rainfall of 0.0 inches.
Is 2022 a wet year in California?
According to a government summary just released, 2022 is the driest first half of any year in California. In data released Monday, NOAA’s National Centers for Environmental Information found that the state’s January through June rainfall was the lowest on record dating back to 1895.
Will California be a drought year 2022?
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), 2022 will be the driest year in California’s 128 years of rainfall records due to exceptionally dry January, February and March.
Is California dry this year?
High temperatures in California this April and early May made 2021 critically dry. Snow melted and runoff evaporated faster in the Sacramento, Feather and American River watersheds. The state continues to monitor drought conditions.
What month in California gets the most rain?
On average, January is the wettest with 6 days of rain/snow. July is the driest month on average with 0 rainy days. The average annual number of rainy days is: 35.
What month in California does it rain?
The rainy season of the year lasts for 6.3 months, from October 16 to April 25, with a rolling 31-day rainfall of at least 0.5 inches. The rainiest month in Los Angeles is February, with an average rainfall of 3.3 inches. The rainfall-free period of the year lasts for 5.7 months, from April 25 to October 16.
What is the rainiest month?
His conclusion is that June is generally the wettest month in the US, with 2,053 out of 8,535 cities reporting it.
What month does California get rain?
July 1 through June 30 is traditionally when California measures its precipitation season, as nearly all rain and snow falls during the winter months. As the state faces a long, hot summer, hopeful eyes are already on November and December.
What month does CA get the most rain?
The rainy season of the year lasts for 6.3 months, from October 16 to April 25, with a rolling 31-day rainfall of at least 0.5 inches. The rainiest month in Los Angeles is February, with an average rainfall of 3.3 inches.
Is 2023 a wet year in California?
Only a small part of the Mid-Atlantic region is expected to have a particularly wet autumn. After November, the likelihood of La Niña continues. By early 2023, there is less than a 50% chance we are still in a La Niña pattern.
Is this an El Niño year 2022?
The WMO predicts a continuation of the current La Niña pattern over the next six months, with a 70 percent probability from September to November 2022, but gradually decreasing to 55 percent from December to February 2022-2023. The current La Niña pattern began in September 2020.
Will La Niña continue in 2022? Forecasters expect La Niña to continue through the summer and into fall and early winter. Equator sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific were mostly below average in June 2022 (blue). A few warm pockets (orange) dotted the far eastern Pacific.
Are we in El Niño?
Current climate: The ENSO phase is currently neutral or waning El Niño.
Is El Niño coming 2022?
The latest IRI cloud forecast of the Niño-3.4 SST index indicates that La Niña will persist in the Northern Hemisphere during the winter of 2022–23 [Fig. 6]. There is an interesting gap between the dynamical and statistical model predictions, with the latter suggesting that La Niña will last longer, through January and March 2023.
Will there be an El Niño in 2022 23?
La Niña is expected to continue, with the chance of La Niña gradually decreasing from 86% to 60% in the December 2022 to February 2023 time frame. Another source of uncertainty is the atmospheric response to La Niña or El Niño.
Will there be an El Niño 2022 23?
The first source of uncertainty is how accurately we can predict La Niño or El Niño. La Niña is expected to continue, with the chance of La Niña gradually decreasing from 86% to 60% during the December 2022 to February 2023 time frame.
Will there be La Niña 2023?
La Niña underway in the tropical Pacific. Most models predict La Niña to subside in early 2023, suggesting a relatively short-lived event; ENSO events typically peak in summer in the Southern Hemisphere and decline in autumn.
Will El Niño ever come back?
El-Nino is expected to arrive as early as the second half of 2022, according to ECMWF estimates, and is very likely to continue throughout 2023, possibly 2024 or even 2025. El-Nino is primarily associated with hot and dry conditions around the world, would occur severe droughts or fires had to occur.
Does San Diego have a monsoon season?

Monsoon season can start as early as July for us in San Diego, but most of the activity is in August and September. Every year is a little different and this year we are getting a little more activity in terms of thunder, lightning and isolated precipitation for our mountains and deserts.
Are thunderstorms common in San Diego? Among the California cities with a mild climate, San Diego stands out as having the least amount of stormy weather. San Diego averages only five days a year with thunderstorms or major storms and never a snowstorm.
Do monsoons happen in California?
Although Northern California is not in the heart of the monsoon, it is close enough to the North American monsoon to see some occasional showers and thunderstorms. Almost every other continent is home to a unique monsoon.
What causes monsoons in California?
Moisture from the Pacific Ocean and Gulf of Mexico creates northward currents. Combine that with the heat of the day in California creating rising air, or low pressure, and the conditions are set for monsoon storms.
Does Southern California have monsoon?
“It’s monsoon season for SoCal,” said Casey Oswant, a meteorologist with the National Weather Service in San Diego. “We’re pulling in a lot of moisture from the Gulf of California.”
Does Southern California have a monsoon season?
“It’s monsoon season for SoCal,” said Casey Oswant, a meteorologist with the National Weather Service in San Diego. “We’re pulling in a lot of moisture from the Gulf of California.”
Is 2022 a wet year in California?
According to a government summary just released, 2022 is the driest first half of any year in California. In data released Monday, NOAA’s National Centers for Environmental Information found that the state’s January through June rainfall was the lowest on record dating back to 1895.
What causes monsoons in California?
Moisture from the Pacific Ocean and Gulf of Mexico creates northward currents. Combine that with the heat of the day in California creating rising air, or low pressure, and the conditions are set for monsoon storms.
Why is San Diego so humid?
NBC 7 meteorologist Sheena Parveen said the additional humidity is being caused by a monsoon weather pattern that is sending air currents from the south across San Diego County. These air currents pick up moisture from the Gulf of Mexico and California and bring it to our region.
Is San Diego dry or humid?
Although we are not exactly near the Mediterranean, San Diego has a Mediterranean climate. We can get hot, sunny and dry summers and winters that are slightly cold and slightly wet. However, San Diego is a bit drier and drier, although temperatures rarely reach (or exceed) 90°F (32°C).
Does San Diego have high humidity?
Humidity and Wind San Diego has some somewhat humid months, with moderately humid months on the other side of the year. The least humid month is January (46.8% relative humidity), and the most humid month is July (66.3%).

